Researchers explore promising treatment for MRSA ‘superbug’
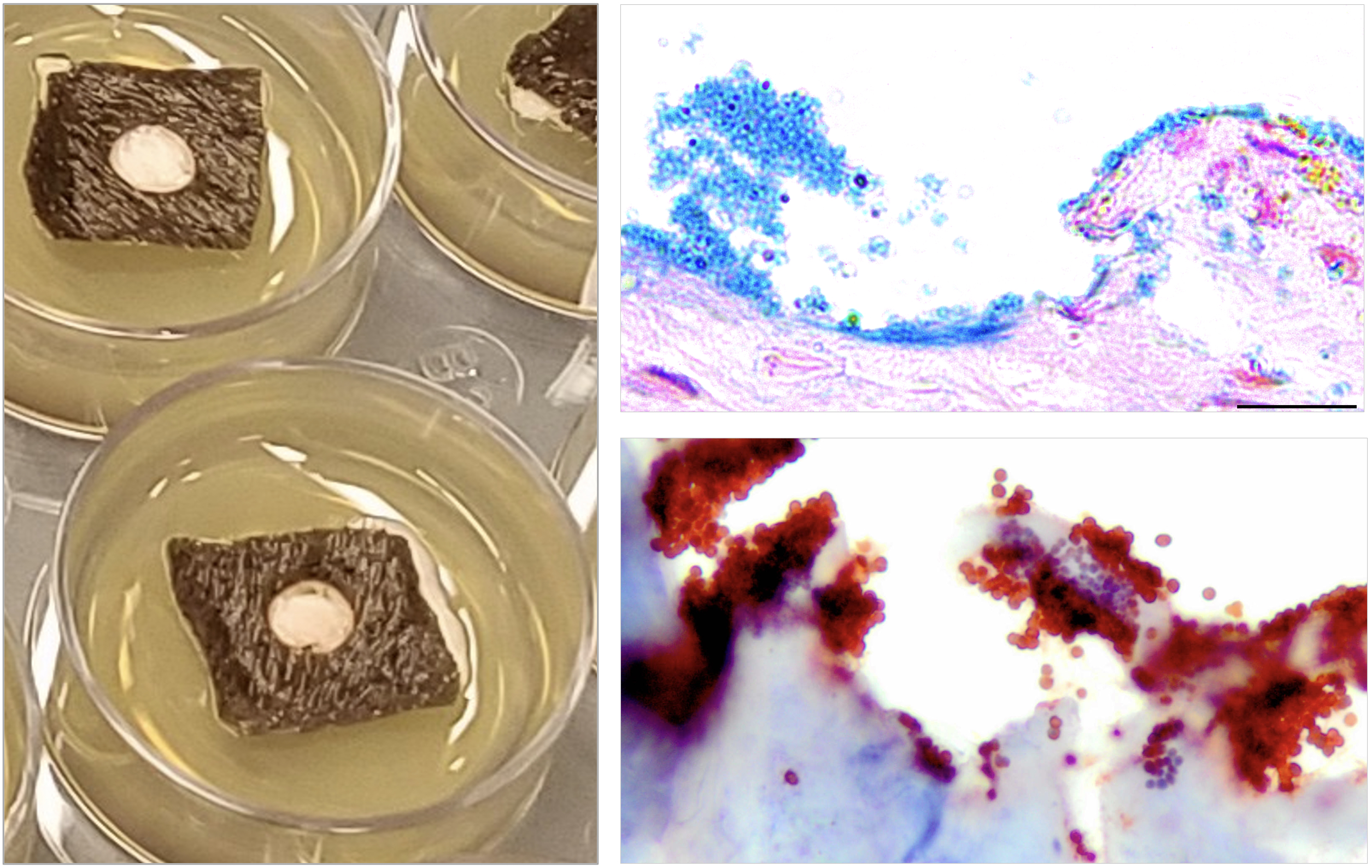
 A new Cornell study has found the antimicrobial properties of certain stem cell proteins could offer a potential treatment to reduce infection in skin wounds.
A new Cornell study has found the antimicrobial properties of certain stem cell proteins could offer a potential treatment to reduce infection in skin wounds.
Treating wounds with the secretion of a type of stem cell effectively reduced the viability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus – better known as MRSA – according to a new study from researchers at the Baker Institute for Animal Health, part of the College of Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Moreover, the secretion stimulated the surrounding skin cells to build up a defense against the bacterial invader, the researchers found. The study appeared Sept. 16 in Stem Cells Translational Medicine.
Read the full article in the September 16, 2021 Cornell Chronicle