Tuberculosis bacteria's trash-eating habit inspires search for new drugs
When hijacking a garbage truck one might as well make use of the trash. That logic drives how tuberculosis-causing bacteria feed, according to Cornell scientists who found that bacteria infecting macrophages – garbage-truck-like immune cells – slow their hosts’ trash-processing abilities to snack on trash they pick up. The study, selected as Editor’s Choice in the journal Cellular Microbiology in June 2013, opens a new road in the search for better drugs to fight tuberculosis.
One of the world’s deadliest diseases, tuberculosis has been the number one killer in many regions at different times throughout history, including the United States. It still infects a third of the world’s population, according to the Centers for Disease Control, and remains a leading killer of people who are infected with HIV. The bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis spread through air to cause the disease in humans and animals, usually attacking the lungs.
Though cases have declined in the United States, other parts of the world are experiencing increased incidence of tuberculosis, and new drug-resistant strains are emerging constantly, raising the stakes in the arms race for treatments.
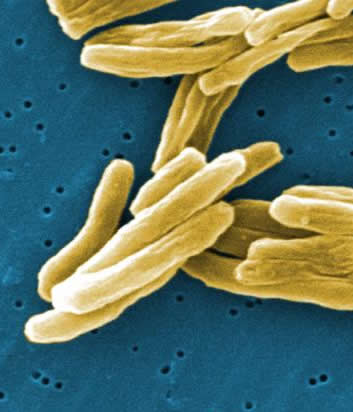
“We are studying how this microbe deals with its host being an immune cell meant to kill microbes,” said microbiologist Dr. David Russell, the William Kaplan Professor of Infection Biology at Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine. “We’ve uncovered several ways the microbe changes the macrophage it infects to ensure its survival. Our lab’s drug-discovery branch is now using this new knowledge to identify molecules that could kill M. tuberculosis inside its host after infection.”
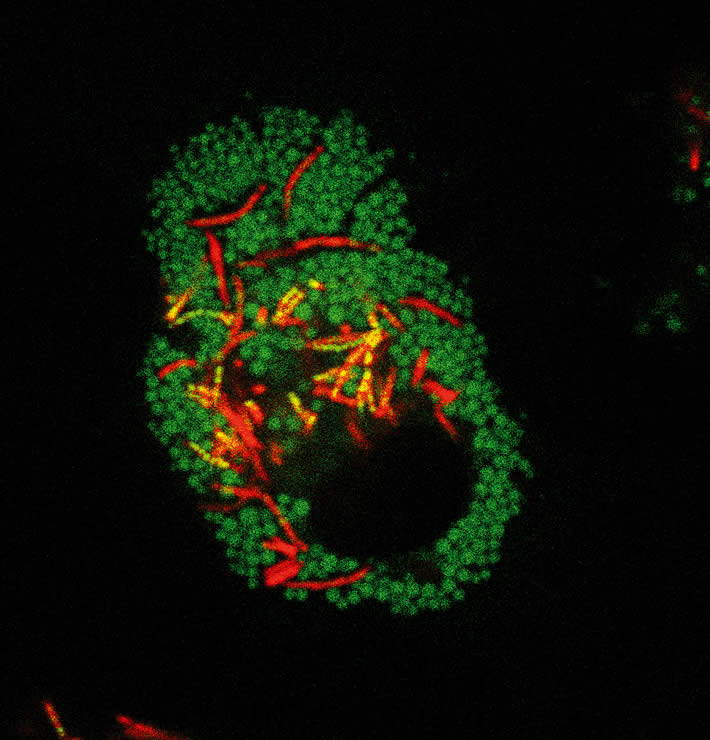
Russell’s lab developed a panel of tests that make real-time fluorescent images and quantitative measures of what’s happening in macrophages – big immune cells that patrol tissues, picking up debris from old or dead cells and sometimes killing microbes they encounter. A macrophage ingests its targets into its phagosome, a stomach-like compartment where it breaks down what it’s picked up.
Important things macrophages pick up include low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), which move fatty lipids including cholesterol through the bloodstream. Too many LDLs, also known informally as “bad cholesterol,” can build plaques in arteries that can cause strokes, heart attacks, and cardiovascular diseases. Macrophages help prevent plaques by consuming LDLs and breaking down their lipids.

But tuberculosis bacteria cripple infected macrophages’ abilities to process lipids, Russell found. Infected macrophages keep lipids in a way they didn’t before, and the bacteria feed on this fatty refuse while slowing the macrophages’ ability to remove plaque-causing LDLs. Images Russell captured caught the bacteria snacking red-handed, showing lipids moving from the macrophage’s phagosome into the bacteria.
“Seeing this process has helped us design our drug-discovery work to better match what’s happening in human tuberculosis,” said Russell. “Now that we have a better understanding of how these bacteria feed, our lab is looking for compounds that can use their feeding strategy against them to starve them or kill them outright to treat people who have been infected.”