Sampling Instructions
Do not submit EDTA or heparin plasma, serum, serum separator or clot activator tubes. These samples are invalid for coagulation screening tests, protein C, or factor assays.
Vacutainer Draw - Large Dogs
Draw blood with a vacutainer needle or butterfly catheter directly into a 3.2% or 3.8% citrate tube (blue top tube) Make sure the tube is in-date and completely filled by vacuum draw.
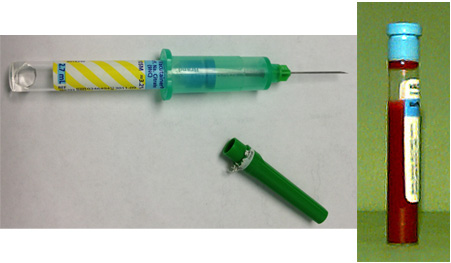
Syringe Draw - Small Dogs/Cats
- Draw an exact volume of citrate into a syringe to obtain 1 of the following total samples:
0.2 ml citrate + 1.8 ml blood = 2.0 ml total
0.3 ml citrate + 2.7 ml blood = 3.0 ml total
0.4 ml citrate + 3.6 ml blood = 4.0 ml total - Perform venipuncture to collect total sample volume.
- Transfer citrated blood sample to a plastic or no-additive glass tube for centrifugation.
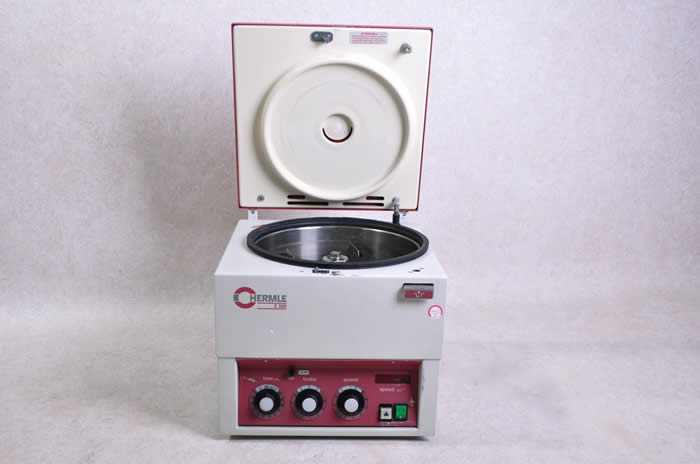

Plasma Separation
- Centrifuge the whole blood sample for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Aspirate plasma and transfer to a plastic or no-additive glass shipping tube.
If clot fragments or hemolysis (unless in vivo hemolysis) –redraw - Refrigerate plasma for same-day shipment or store frozen for up to 2 weeks.
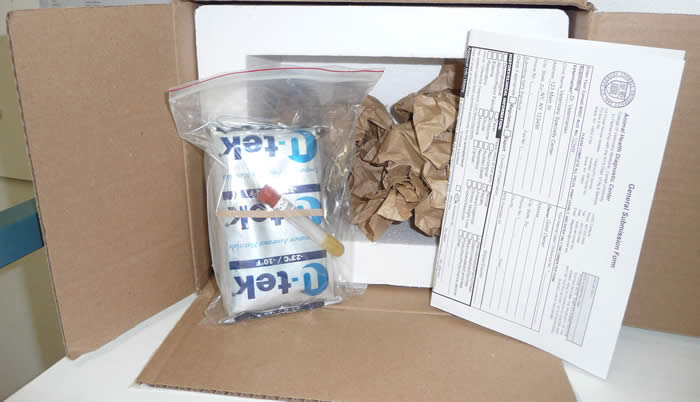

Shipping
- Ship for overnight delivery on frozen cold packs.
- Place the cold pack and sample tube in a plastic bag
Afix tube to cold pack with rubber band, wrap carefully to prevent breakage - Fill all dead space with crumpled paper or bubble wrap
- Complete an AHDC submission form, place in the outer box
Sampling Instructions
Collection Method 1: Vacutainer method
Materials: 3.0 ml sodium citrate (blue top) Vacutainer tube, Vacutainer needle or Vacutainer butterfly (22 or 21gauge), dilute nolvasan or antiseptic wipe,
Options: either 3.8% or 3.2% sodium citrate tubes can be used, larger volume (4 to 5 ml draw) tubes can be used for big (>50 lb.) dogs, hair overlying venipuncture site can be clipped
Procedure:
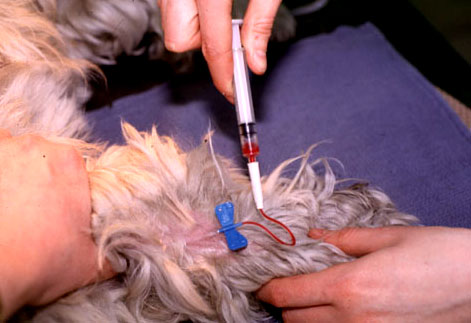
- Gently restrain the patient and apply manual pressure proximal to the cephalic or saphenous venipuncture site to allow the vein to fill with blood.
- Perform venipuncture using the Vacutainer needle or butterfly
- Attach the tube and allow blood to fill the tube completely by vacuum
- Withdraw the needle and apply direct pressure to the venipuncture site
Collection Method 2: Syringe method
Materials: sodium citrate anticoagulant, 3.0 ml syringe, 22 or 21 gauge needle or 22 or 21 gauge short tubing butterfly catheter (short tubing = 3.5 inches), dilute nolvasan solution or antiseptic wipe
Options: either 3.8% or 3.2% sodium citrate can be used, larger volume (6 ml syringe could be used to collect 4 to 6 ml sample volume) hair overlying venipuncture site can be clipped
Procedure:
- Gently restrain the patient and apply manual pressure proximal to cephalic or saphenous venipuncture site to allow the vein to fill with blood.
- Aspirate an exact volume of citrate into the collection syringe to give a final ratio of 1 part citrate to 9 parts blood. Use one of the following sampling protocols:
2.0 ml total sample volume = 0.2 ml citrate + 1.8 ml blood
3.0 ml total sample volume = 0.3 ml citrate + 2.7 ml blood
4.0 ml total sample volume = 0.4 ml citrate + 3.6 ml blood - Perform venipuncture and collect blood into the syringe containing pre-measured citrate to obtain the exact total sample volume.
- Withdraw the needle and apply direct pressure to the venipuncture site
- Remove the needle from the collection syringe and gently express the blood sample into a plastic tube.
Notes on Collection Methods
- Use of peripheral veins, rather than the jugular vein, is preferred for patients having severe hemostatic defects because of the risk of hematoma formation at venipuncture sites. Cervical hematoma formation could compromise the patient’s airway.
- Blood samples can be drawn from an indwelling catheter using the syringe method, if the catheter is first flushed with 5 to 10 ml. sterile saline (0.9% saline, NO HEPARIN). A 3 to 5 ml aliquot of blood should be withdrawn from the catheter, and then the sample syringe containing pre-measured citrate is attached to the catheter and blood is withdrawn to obtain the exact total sample volume.
- Atraumatic venipuncture technique is critical to prevent activation/depletion of clotting factors during collection.
- The ratio of citrate to blood is critical for valid results. The sample should be redrawn if the Vacutainer tube or syringe is not filled to the desired sample volume.
- Sodium citrate (3.2 or 3.8%) is the only acceptable anticoagulant for coagulation assays. Samples drawn into EDTA, heparin, or other anticoagulants or samples drawn into clot activator or serum separator tubes are invalid for coagulation testing.
Processing Instructions for Coagulation Assays
Materials: Tabletop centrifuge, plastic pipettes or TB syringes, plastic tubes with secure caps, waterproof marker for labeling.
Procedure:
- Centrifuge the citrate whole blood sample tube for 10 to 15 minutes at high speed (>2,500 g).
- Aspirate the supernatant plasma with a plastic pipette or TB syringe and transfer the plasma to a clean empty plastic tube.
- Label the sample tube with patient identifiers.
- Transport the sample to the testing laboratory within 1/2 hr of processing or store the sample frozen until transport or shipment to the testing laboratory.
Notes on Processing Methods
- Siliconized glass tubes can be used as centrifugation and storage tubes, however glass tubes may crack, or shatter.
- The presence of clots or clot fragments in the sample is an indication of improper blood collection. Hemolyzed plasma is an indication of improper sampling, unless the patient has a hemolytic disease process. Samples should be redrawn for valid results.